Ferromagnetism Concepts and Applications
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science, Other
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the magnetic field inside a solenoid when a ferromagnetic material is inserted?
It remains the same.
It disappears.
It becomes weaker.
It becomes stronger.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
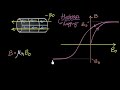
What is the hysteresis graph used to illustrate?
The relationship between electric and magnetic fields.
The thermal conductivity of metals.
The lag of the magnetic field inside a ferromagnet behind the vacuum field.
The speed of light in different materials.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the magnetic domains in a ferromagnet as the vacuum field increases?
They become randomly oriented.
They align in the direction of the field.
They shrink in size.
They disappear.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the saturation point in the context of ferromagnets?
The point where the magnetic field inside is zero.
The point where the magnetic field inside is negative.
The point where all domains are aligned and the field cannot increase further.
The point where the vacuum field is maximum.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What property of ferromagnets prevents the magnetic field inside from returning to zero when the vacuum field is reduced?
Conductivity
Retentivity
Permeability
Elasticity
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What occurs when the vacuum field is reversed in direction?
The magnetic field inside becomes zero immediately.
The domains align randomly.
The magnetic field inside decreases and can become negative.
The magnetic field inside remains unchanged.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the area under the hysteresis curve represent?
The maximum vacuum field strength.
The speed of domain alignment.
The energy loss as heat.
The total magnetic field strength.
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Magnetic Fields and Solenoids Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Imanes y electromagnetismo: video de evaluación
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Magnetism: Magnetism in Our Solar System
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Earth's Magnetic Field and Solar Activity
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Exploring Magnetic Fields and Field Lines
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Magnetic Fields and Electric Currents
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

6 questions
What Are Magnets?: Magnetic Fields
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Magnetic Field Calculations in Coils
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Brand Labels
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Core 4 of Customer Service - Student Edition
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

15 questions
What is Bullying?- Bullying Lesson Series 6-12
Lesson
•
11th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

38 questions
Forces and Free-body Diagrams Practice
Quiz
•
9th Grade

14 questions
Distance & Displacement
Quiz
•
11th Grade

20 questions
Calculating Net Force
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

18 questions
NEW Acceleration Tables
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 4.1 - Destructive Processes
Quiz
•
9th Grade

35 questions
Waves Practice Test
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 4.2 - Constructive Forces
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 4.3 - Conservation of Momentum
Quiz
•
9th Grade