AP Physics 1: Rotation - Newton's Second Law
Interactive Video
•
English
•
10th Grade
•
Hard

Brandon Lopez
FREE Resource
5 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
He's giving an incomplete definition right now, but let's review the complete definition. Rotational Inertia (or "moment of inertia") depends on mass AND...
How that mass is distributed
Gravity
Force
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
He just increased the net torque. What should this do to the slope of the angular velocity vs. time graph?
Increase it
Decrease it
It should remain the same
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
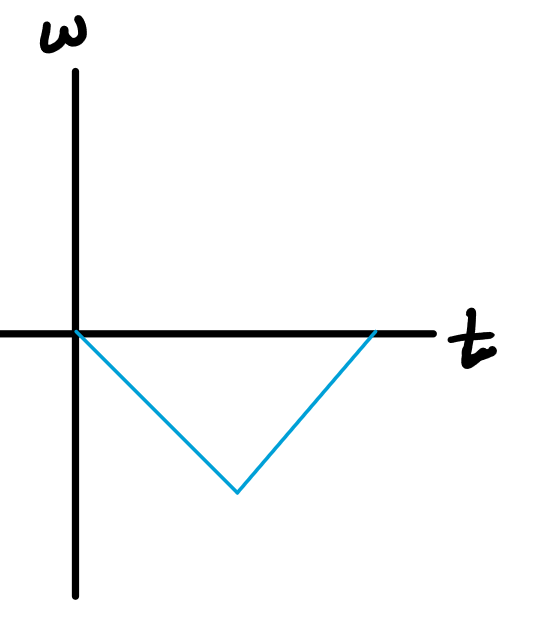
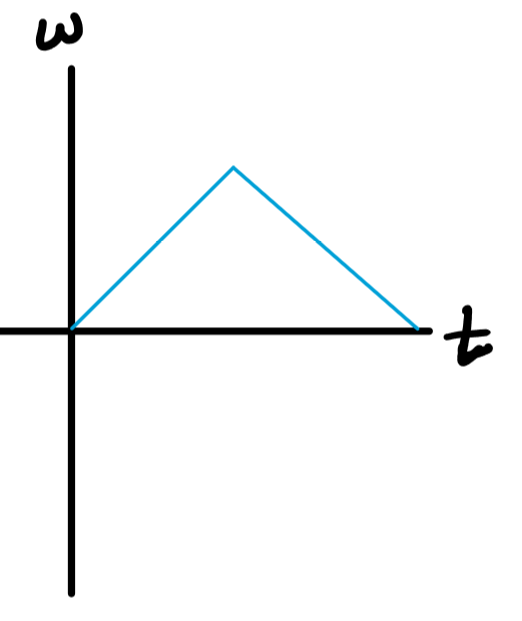
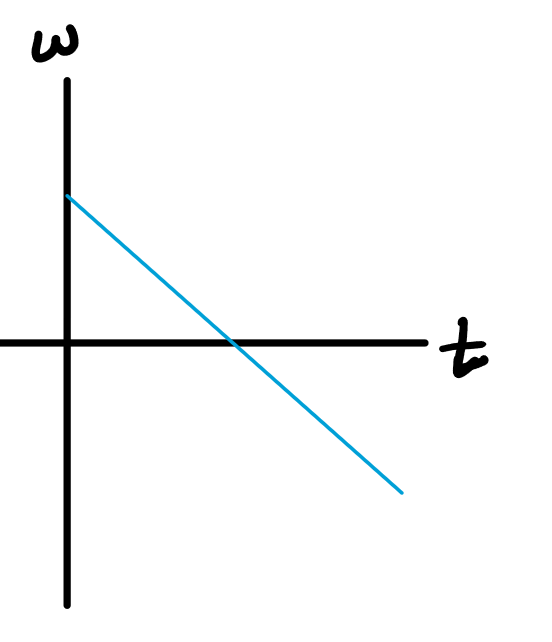
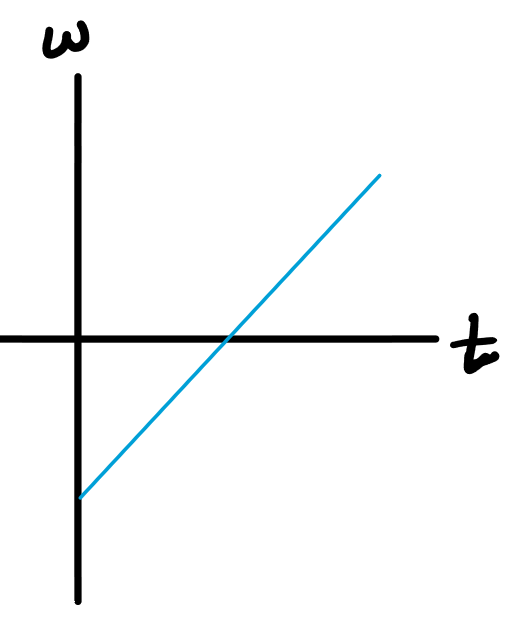
From the sensor's "point of view", the turn table started at rest, began to turn CW while speeding up, then started slowing down (when the mass bounced off the floor) while still spinning CW. What would the angular velocity vs. time graph look like?
b
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
The moment of inertia of a solid disk is . If an object is added on top of it and the object has a mass of mobj and is placed a distance "d" from the center of the disk, what would be the total moment of inertia of the disk and object?
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How can he decrease the rotational inertia (and therefore increase the angular acceleration) while still having "Edna" "ride" on the disk?
Move "Edna" closer to the center
Move "Edna" further from the center
It isn't possible without using a smaller mass
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
CLEAN : Mexican teachers block the Senate
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Mass and Weight
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

8 questions
How to Write About Poetry: I Shall Forget You Presently
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Rotational Motion and Energy Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Things in Motion: Inertia
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

2 questions
How to Write About Poetry: I Shall Forget You Presently
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

5 questions
Shakespeare's Greatest Love Poem: Let me not to the marriage of true minds
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

3 questions
Mass and Weight
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

20 questions
Brand Labels
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Ice Breaker Trivia: Food from Around the World
Quiz
•
3rd - 12th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
ELA Advisory Review
Quiz
•
7th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Multiplication and Division Unknowns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for English

12 questions
PSAT Week 1
Quiz
•
8th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Figurative Language Review
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Figurative Language Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Identifying Common and Proper Nouns
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Analyzing Author's Purpose in Nonfiction Texts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Identifying and Using Sentence Structures
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Finding the Theme of a Story
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Mastering Subject-Verb Agreement
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade