Punnett Square and Genetic Ratios
Interactive Video
•
Biology
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary purpose of a Punnett square?
To analyze the behavior of animals
To determine the lifespan of organisms
To calculate the exact number of offspring
To predict the outcomes of genetic crosses
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which rule is essential when setting up a Punnett square?
Rule of multiplication
Rule of addition
Rule of segregation
Rule of dominance
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does a phenotype ratio describe?
The lifespan of an organism
The number of offspring produced
The physical appearance of an organism
The genetic makeup of an organism
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the genotype of a homozygous dominant organism?
One dominant allele
Two recessive alleles
One dominant and one recessive allele
Two dominant alleles
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a heterozygous cross, what is the expected phenotype ratio for a dominant and recessive trait?
25% dominant, 75% recessive
75% dominant, 25% recessive
50% dominant, 50% recessive
100% dominant
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
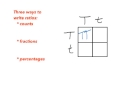
How can genotype ratios be expressed?
As counts, fractions, or percentages
Only as percentages
Only as counts
Only as fractions
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does a genotype ratio of 1:2:1 indicate in a heterozygous cross?
1 homozygous dominant, 2 homozygous recessive, 1 heterozygous
1 homozygous recessive, 2 heterozygous, 1 homozygous dominant
1 heterozygous, 2 homozygous dominant, 1 homozygous recessive
1 homozygous dominant, 2 heterozygous, 1 homozygous recessive
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Genetic Vocabulary and Punnett Squares in Mouse Breeding
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Genotype and Phenotype: Mastering the Punnett Square for Genetic Predictions
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Probability and Genetics Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Dihybrid Cross and Genetic Principles
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Genetics Probability and Punnett Squares
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Genetic Probability and Diagrams
Interactive video
•
8th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Monohybrid Crosses and Ratios
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Genotypes And Phenotypes In Genetics Explained
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

20 questions
Brand Labels
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Ice Breaker Trivia: Food from Around the World
Quiz
•
3rd - 12th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
ELA Advisory Review
Quiz
•
7th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Multiplication and Division Unknowns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell Transport
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell organelles and functions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

22 questions
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

25 questions
photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Quiz
•
9th Grade

16 questions
AP Biology: Unit 1 Review (CED)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Biomolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade