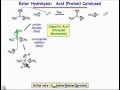
Proton-Catalyzed Reaction Mechanisms
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry
•
11th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are the products of the ester hydrolysis reaction?
Carboxylic acid and ester
Ester and water
Carboxylic acid and methanol
Methanol and water
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of the zwitterionic intermediate in the uncatalyzed reaction?
It speeds up the reaction
It is the final product
It is a temporary charged species
It acts as a catalyst
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which step is considered the rate-determining step in the uncatalyzed reaction?
Formation of zwitterionic intermediate
β elimination
Proton transfer
Nucleophile addition
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is the concentration of the key intermediate expressed in the rate law derivation?
Directly measured
Using fast equilibrium assumptions
Estimated from final products
Ignored in calculations
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What assumption is made about the backward reaction in the simplification process?
It is equal to the forward reaction
It is negligible
It is faster than the forward reaction
It is the main focus of the study
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the proton-catalyzed reaction, what role does the proton play?
It is the final product
It speeds up the rate-determining step
It is a reactant in the stoichiometry
It is consumed and not regenerated
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does the proton affect the electrophile in the catalyzed reaction?
It weakens the electrophile
It converts the electrophile into a nucleophile
It makes the electrophile stronger
It has no effect
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

8 questions
Elementary Reactions
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Decomposition of NH3 and Rate Constants
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Nucleophiles, Electrophiles, Leaving Groups, and the SN2 Reaction
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Spectrophotometry and Reaction Kinetics
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Kinetics: Chemistry's Demolition Derby - Crash Course Chemistry
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

8 questions
The Reaction Path
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Reaction Rates and Rate Laws
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Brand Labels
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Core 4 of Customer Service - Student Edition
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

15 questions
What is Bullying?- Bullying Lesson Series 6-12
Lesson
•
11th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

20 questions
Naming Covalent Compounds
Quiz
•
11th Grade

20 questions
Atomic Structure
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Electron Configurations and Orbital Notation
Quiz
•
11th Grade

12 questions
Significant figures
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Naming Ionic Compounds
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

18 questions
Ions
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Lewis Dot Structures
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

71 questions
Periodicity Test Prep
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade