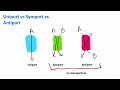
Transport Mechanisms in Cell Membranes
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Chemistry
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are the three types of protein channels discussed in the video?
Uniport, Symport, Antiport
Uniport, Biport, Triport
Symport, Antiport, Biport
Uniport, Triport, Quadport
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of a uniport channel?
To move three molecules simultaneously
To move two molecules in opposite directions
To move two molecules in the same direction
To move a single molecule in one direction
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a symport channel, how do the molecules move?
In the same direction
Randomly
In opposite directions
One molecule moves while the other stays
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What distinguishes an antiport channel from other types?
It moves molecules in the same direction
It moves a single molecule
It does not move molecules
It moves molecules in opposite directions
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which channel type is exemplified by the sodium-potassium pump?
Uniport
Symport
Antiport
Biport
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How many sodium ions are moved out in the sodium-potassium channel example?
One
Two
Three
Four
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is an example of a symport channel mentioned in the video?
Sodium-potassium pump
Glucose transport with sodium
Calcium channel
Chloride channel
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

20 questions
Brand Labels
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

11 questions
NEASC Extended Advisory
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Ice Breaker Trivia: Food from Around the World
Quiz
•
3rd - 12th Grade

10 questions
Boomer ⚡ Zoomer - Holiday Movies
Quiz
•
KG - University

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Multiplication and Division Unknowns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Multiplying and Dividing Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell Transport
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell organelles and functions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

25 questions
photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Quiz
•
9th Grade

15 questions
Enzymes
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Macromolecules
Quiz
•
10th Grade

15 questions
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: Key Concepts and Differences
Interactive video
•
9th Grade