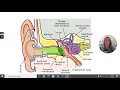
Ear Anatomy and Hearing Loss Concepts
Interactive Video
•
Science, Biology, Physics
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary reason sound cannot travel through space?
Space is too vast.
Space lacks matter.
Space is too cold.
Space is too dark.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does the frequency of a sound wave affect its pitch?
Higher frequency results in a lower pitch.
Frequency does not affect pitch.
Lower frequency results in a higher pitch.
Higher frequency results in a higher pitch.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What part of the ear first receives sound waves from the environment?
Auditory nerve
Cochlea
Eardrum
Pinna
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which part of the ear is responsible for converting sound vibrations into nerve signals?
Auditory canal
Cochlea
Eardrum
Pinna
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the medical term for an ear infection occurring in the middle ear?
Otitis interna
Otitis superior
Otitis media
Otitis externa
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a common symptom of conductive hearing loss?
Ringing in the ears
Complete deafness
Sharp ear pain
Muffled hearing
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main cause of sensorineural hearing loss?
Fluid buildup in the ear
Eardrum perforation
Nerve damage
Earwax blockage
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Otolaryngology and Eye Care Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Anatomy and Function of the Ear
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Sound Waves and Loudness
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

3 questions
¿Qué es el sonido?: sonido y seguridad
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
What Is Sound?: Summing Up
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Balance and the Ear Anatomy
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Hearing and Sound Wave Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Understanding the Tensor Tympani Muscle
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

20 questions
Brand Labels
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Ice Breaker Trivia: Food from Around the World
Quiz
•
3rd - 12th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
ELA Advisory Review
Quiz
•
7th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Multiplication and Division Unknowns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Science

10 questions
Exploring Newton's Laws of Motion
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Chemical and Physical Changes
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the States of Matter
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the States of Matter and Thermal Energy
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Light and Waves Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

16 questions
3.4 Biogeochemical Cycles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

21 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition Processes
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade