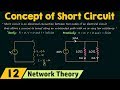
Understanding Short Circuits and Current Behavior
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science, Mathematics
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a short circuit?
A desired connection between two nodes
An abnormal connection with high resistance
A normal connection in an electrical circuit
An unintended path with low or zero resistance
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In an ideal short circuit, what is the resistance of the unintended path?
Very high
Equal to the voltage
Zero
Infinite
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is the current infinite in an ideal short circuit?
Because the voltage is zero
Because the resistance is infinite
Because the resistance is zero
Because the voltage is infinite
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is the ideal short circuit not practically possible?
It violates the law of conservation of energy
It requires infinite resistance
It requires infinite voltage
It violates Ohm's Law
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a practical short circuit, what is the nature of the current?
Infinite
Finite
Negative
Zero
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the resistance of the unintended path in a practical short circuit?
Zero
Infinite
Very high
Equal to the voltage
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the practical example, what is the voltage source used?
100 volts
5 volts
50 volts
10 volts
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Resistors And Capacitors In Circuit Dynamics
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Wheatstone Bridge
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Voltage Divider Circuit Concepts
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Digital Tester Measurement Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Electric Circuit Concepts and Principles
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Electric Circuits and Ohm's Law
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Voltage, Current, and Resistance
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Circuit Components and Functions
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Brand Labels
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Core 4 of Customer Service - Student Edition
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

15 questions
What is Bullying?- Bullying Lesson Series 6-12
Lesson
•
11th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

38 questions
Forces and Free-body Diagrams Practice
Quiz
•
9th Grade

14 questions
Distance & Displacement
Quiz
•
11th Grade

20 questions
Calculating Net Force
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

18 questions
NEW Acceleration Tables
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 4.1 - Destructive Processes
Quiz
•
9th Grade

35 questions
Waves Practice Test
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 4.2 - Constructive Forces
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 4.3 - Conservation of Momentum
Quiz
•
9th Grade