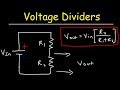
Circuit Analysis and Voltage Dividers
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Aiden Montgomery
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the total resistance in a series circuit with resistors of 10 ohms and 20 ohms?
40 ohms
20 ohms
30 ohms
10 ohms
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Using Ohm's Law, how do you calculate the current in a circuit with a 12V battery and 30 ohms of resistance?
12*30 amps
12+30 amps
12/30 amps
30/12 amps
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a voltage divider circuit with equal resistors, what is the output voltage if the input is 12 volts?
6 volts
12 volts
9 volts
3 volts
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the total resistance required for a circuit with a 20V battery and 50 milliamps of current?
200 ohms
300 ohms
500 ohms
400 ohms
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does connecting a device with internal resistance affect the voltage across R2 in a voltage divider?
Increases the voltage
Decreases the voltage
No change in voltage
Doubles the voltage
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the voltage across R2 if the internal resistance of a connected device is decreased?
Voltage remains the same
Voltage doubles
Voltage decreases
Voltage increases
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
For minimal voltage change, how should the internal resistance of a device compare to R2 in a voltage divider?
10 times greater than R2
100 times greater than R2
Less than R2
Equal to R2
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Understanding Battery Internal Resistance and Terminal Voltage
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Calculating Current and Voltage in Series and Parallel Circuits
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Insulation Resistance Testing Procedures
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

11 questions
Circuit Analysis Techniques and Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Thevenin Equivalent Circuit Concepts
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
OHM's Law
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Analyzing Circuit Resistance and Current Flow in Electrical Systems
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Understanding Electric Circuits: Series, Parallel, and Short Circuits
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University
Popular Resources on Wayground

20 questions
Brand Labels
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Ice Breaker Trivia: Food from Around the World
Quiz
•
3rd - 12th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
ELA Advisory Review
Quiz
•
7th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Multiplication and Division Unknowns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

25 questions
Newton's Laws of Motion
Quiz
•
9th Grade

15 questions
Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

73 questions
S1 Interim Review Physics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Calculating Net Force
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

18 questions
Net Forces
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Position vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
9th Grade

37 questions
Forces-Conceptual Physics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

32 questions
Unit 3 EM Spectrum Quizizz Review - 2025/2026
Quiz
•
9th Grade