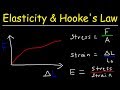
Understanding Hooke's Law and Material Properties
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Liam Anderson
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does Hooke's Law state about the relationship between force and the change in length of a solid?
Force is unrelated to the change in length.
Force is equal to the change in length.
Force is inversely proportional to the change in length.
Force is proportional to the change in length.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the significance of the proportional limit on a force versus change in length graph?
It indicates the maximum force the material can withstand.
It shows the point where the material becomes elastic.
It is the point up to which Hooke's Law is valid.
It marks the point where the material breaks.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to a material when it is in the plastic region?
It returns to its original shape.
It becomes permanently deformed.
It breaks into two pieces.
It stretches infinitely.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the context of stress and strain, what is Young's modulus?
The ratio of area to force.
The ratio of force to area.
The ratio of stress to strain.
The ratio of strain to stress.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the relationship between stress and area when a force is applied?
Stress increases as area increases.
Stress is equal to area.
Stress decreases as area increases.
Stress is independent of area.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does a high elastic modulus affect a material's response to force?
The material will stretch more easily.
The material will compress more easily.
The material will change length less.
The material will break more easily.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which material property is indicated by a high Young's modulus?
Elasticity
Flexibility
Strength
Brittleness
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Testing and Properties of Ceramics
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

2 questions
Understanding Stress and Strain in Mechanics
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

11 questions
Understanding Stellar Magnitudes and Brightness
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Stress Analysis and Soderbergh Criteria
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

11 questions
Plate Tectonics and Geological Folds Explained
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
The Role and Limitations of Scientific Models in Understanding Matter
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Engineering Challenges and Solutions
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Stress-Strain Diagrams and Material Behavior
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
UPDATED FOREST Kindness 9-22
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
US Constitution Quiz
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

20 questions
Position vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
9th Grade

25 questions
Newton's Laws of Motion
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Claim Evidence Reasoning
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

14 questions
Distance & Displacement
Quiz
•
11th Grade

17 questions
Free Body Diagrams
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 3.3 - Universal Gravitation
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Motion Graphs
Quiz
•
11th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 3.4 - Moon's Orbit
Quiz
•
9th Grade