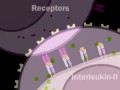
Understanding the Humoral Immune Response
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Medium
Aiden Montgomery
Used 2+ times
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of Class 2 MHC proteins in the humoral immune response?
They produce antibodies.
They bind antigen fragments and display them on the cell surface.
They destroy antigens directly.
They activate B-cells.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the initial step in the humoral immune response?
Release of interleukin-2.
Production of antibodies by plasma cells.
Engulfing and processing of an antigen by a macrophage.
Activation of B-cells.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens when a helper T-cell binds to a displayed antigen?
The T-cell becomes inactive.
The T-cell engulfs the antigen.
The T-cell releases antibodies.
The antigen-presenting cell releases interleukin-1.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the function of interleukin-2 in the immune response?
It triggers helper T-cells to divide.
It destroys antigens.
It binds to antigens.
It deactivates B-cells.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the daughter cells produced by helper T-cells?
They become macrophages.
They produce a clone identical to the first T-cell.
They attack antigens directly.
They deactivate B-cells.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
During the effector phase, what role do activated helper T-cells play?
They help B-cells develop into plasma cells.
They directly attack pathogens.
They produce interleukin-1.
They become antigen-presenting cells.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How do B-cells become antigen-presenting cells?
By producing antibodies.
By engulfing antigens directly.
By releasing interleukin-2.
By processing antigens and displaying them with Class 2 MHC proteins.
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
Peanut Patch' could cure peanut allergies in children
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

6 questions
Hybridoma Technology Quiz
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
CLEAN : New paths to cure cancer emerge from immunotherapy trials
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Immune System Functions and Responses
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Immune System Memory and Response
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Immune System Concepts and Functions
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Types of Immune Cell Receptors
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

6 questions
TED: How we could teach our bodies to heal faster | Kaitlyn Sadtler
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University
Popular Resources on Wayground

20 questions
Brand Labels
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Ice Breaker Trivia: Food from Around the World
Quiz
•
3rd - 12th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
ELA Advisory Review
Quiz
•
7th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Multiplication and Division Unknowns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Cell organelles and functions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

16 questions
AP Biology: Unit 1 Review (CED)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Macromolecules
Quiz
•
10th Grade

16 questions
AP Biology: Unit 2 Review (CED)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Cell Transport
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
AP Bio Insta-Review Topic 2.1*: Cell Structure - Subcellular Com
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
AP Biology Unit 2 Review Qs
Quiz
•
12th Grade

10 questions
Quick10Q: Organelles
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade