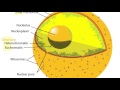
Nuclear Membrane Functions and Structure
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science
•
6th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Sophia Harris
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of the nuclear membrane?
To transport proteins
To produce energy for the cell
To store nutrients
To keep DNA inside the nucleus
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is another name for the nuclear membrane?
Plasma membrane
Nuclear envelope
Cell wall
Cytoplasmic membrane
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which part of the nuclear membrane is covered in ribosomes?
Inner membrane
Outer membrane
Nuclear pores
Nuclear lamina
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of nuclear pores?
To produce ribosomes
To provide structural support
To allow materials to move in and out of the nucleus
To store genetic information
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What provides support and strengthens the nuclear envelope?
Nuclear pores
Nuclear lamina
Ribosomes
Cytoplasm
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Where is the nuclear membrane located?
Outside the cell membrane
Inside the mitochondria
Inside the nucleus
Inside the cell membrane but outside the nucleus
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is the nuclear membrane important for the cell?
It synthesizes proteins
It stores waste products
It keeps the nucleoplasm separate from the cytoplasm
It produces energy
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Exploring Meiosis and Cell Division
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Differentiating Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring Cell Structure and Function
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring Cell Wall and Membrane Structures
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Cell Structure and Function Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Cell Structure and Function Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Understanding Telophase in Mitosis
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Brand Labels
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Core 4 of Customer Service - Student Edition
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

15 questions
What is Bullying?- Bullying Lesson Series 6-12
Lesson
•
11th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell organelles and functions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

16 questions
AP Biology: Unit 1 Review (CED)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
Macromolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

15 questions
Enzymes
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
The Cell Cycle
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Macromolecules
Quiz
•
10th Grade