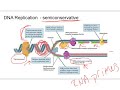
Exploring DNA Structure and Replication
Interactive Video
•
Biology
•
6th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Ethan Morris
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary role of DNA in most organisms?
To store and transmit genetic information
To provide energy for cellular processes
To act as a structural component of cells
To catalyze biochemical reactions
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How are chromosomes typically structured in prokaryotic organisms?
Single-stranded
Circular
Double-stranded
Linear
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are plasmids?
Small, circular, extra-chromosomal DNA
Main chromosomes in eukaryotic cells
Linear DNA fragments in prokaryotes
RNA molecules involved in protein synthesis
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which sugar is found in the structure of DNA?
Fructose
Glucose
Deoxyribose
Ribose
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In RNA, which base pairs with adenine?
Thymine
Cytosine
Guanine
Uracil
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What type of bond holds the base pairs together in DNA?
Peptide bonds
Hydrogen bonds
Ionic bonds
Covalent bonds
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does 'semi-conservative' mean in the context of DNA replication?
New DNA molecules are identical to the original
DNA replication occurs only in one direction
Each new DNA molecule consists of one old and one new strand
Both strands of the original DNA are conserved
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
Endosymbiotic Theory Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Understanding DNA Replication
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
DNA and RNA: Similarities and Differences
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Central Dogma of Biology Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Exploring the Seven Characteristics of Life
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring the Scientific Method in Biology
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring Heredity and Traits
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding the Sense of Smell
Interactive video
•
7th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

54 questions
Analyzing Line Graphs & Tables
Quiz
•
4th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

14 questions
Ecological Succession: Primary and Secondary
Quiz
•
9th Grade

22 questions
Human Body Systems Overview
Quiz
•
9th Grade

25 questions
photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Quiz
•
9th Grade

21 questions
Meiosis Vs Mitosis
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Adaptations and Natural Selection
Quiz
•
7th Grade

10 questions
Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis: Key Differences and Stages
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

13 questions
Amoeba Sisters Viruses Video quiz
Interactive video
•
9th Grade