
HBS 3.1 New
Quiz
•
Science
•
10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Standards-aligned

Lisa Thompson
FREE Resource
Enhance your content in a minute
13 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
Which type of vessels have the smallest diameter?
arteries
venules
capillaries
arterioles
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
Which of the following would decrease blood pressure?
increased viscosity
increased vessel radius
increased blood volume
increased cardiac output
Tags
NGSS.HS-LS1-3
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
An electrocardiogram measures what?
The amount of pressure exerted on blood vessels.
The electrical activity of the heart.
How many times the heart contracts over time.
The body's temperature caused by friction of blood in vessel.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt

The p-wave correlates with which event?
atrium contraction /signals moving from SA node to AV node
ventricle contraction
ventricle repolarization
both atrial and ventricle contraction
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt

The t-wave correlates with which event?
atrium contraction /signals moving from SA node to AV node
ventricle contraction
ventricle repolarization
both atrial and ventricle contraction
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
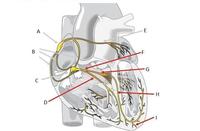
The AV node is located at...
A
B
C
D
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt

The Purkinje fibers are located at...
F
G
H
I
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Phy Sci Q3 Lesson 3
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Biological and health psychology
Quiz
•
11th Grade

11 questions
Carbon-based molecules
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
CONVERGENT BOUNDARY
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
SDG Intro Test
Quiz
•
12th Grade

11 questions
Gears
Quiz
•
University

10 questions
Our Future
Quiz
•
KG - 12th Grade

13 questions
Atomic Structure
Quiz
•
7th Grade - University
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Forest Self-Management
Lesson
•
1st - 5th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

30 questions
Thanksgiving Trivia
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

30 questions
Thanksgiving Trivia
Quiz
•
6th Grade

11 questions
Would You Rather - Thanksgiving
Lesson
•
KG - 12th Grade

48 questions
The Eagle Way
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Identifying equations
Quiz
•
KG - University

10 questions
Thanksgiving
Lesson
•
5th - 7th Grade
Discover more resources for Science

10 questions
Turkey Trouble: A Thanksgiving Adventure
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

50 questions
Review for HS LS 3-1 Test
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Light and Waves Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

13 questions
Post Thanksgiving Review
Lesson
•
9th - 10th Grade

12 questions
Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
Quiz
•
7th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Thermal Energy and Temperature Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the Dynamics of Ocean Currents
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Newton's Third Law: Action and Reaction
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

