Introduction to Chemical Bonding
Quiz
•
Chemistry
•
9th Grade
•
Easy
Standards-aligned

Charles Martinez
Used 3+ times
FREE Resource
15 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
Typically, atoms are more stable when they are
bonded together
apart from each other
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
Why do atoms bond?
They typically don't bond
To add or take away energy levels
To have a full valance shell.
To have a full inner shell
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS1-1
NGSS.HS-PS1-2
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
Ionic bonding is between a
nonmetal and nonmetal
metal and nonmetal
metal and metal
Depends on the situation
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS1-3
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
20 sec • 1 pt
Covalent bonding is between a
nonmetal and nonmetal
metal and nonmetal
metal and metal
It depends on the situation
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
20 sec • 1 pt

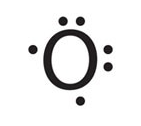
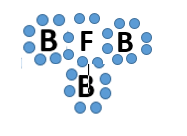
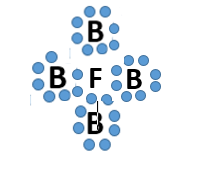
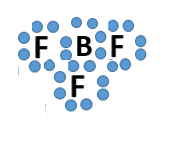
Which bond does this picture best represent?
Metallic bond
ionic bond
covalent bond
James Bond
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
20 sec • 1 pt
What do positive ions tend to do?
lose electrons
gain electrons
lose protons
gain protons
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
20 sec • 1 pt
What happens when magnesium loses 2 electrons?
It stabilizes to a net charge of 0
It turns into an atom
It becomes negatively charged
It becomes positively charged
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS1-2
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Quizizz

10 questions
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
Quiz
•
7th - 12th Grade

18 questions
Chemical Bonding
Quiz
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Ionic vs. Covalent Bonds
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Ionic vs Covalent
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Naming & Writing Chemical Compounds
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Bonding
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

12 questions
chemical bonds
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Types of Bonds
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Quizizz

15 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
4th Grade

20 questions
Math Review - Grade 6
Quiz
•
6th Grade

20 questions
math review
Quiz
•
4th Grade

5 questions
capitalization in sentences
Quiz
•
5th - 8th Grade

10 questions
Juneteenth History and Significance
Interactive video
•
5th - 8th Grade

15 questions
Adding and Subtracting Fractions
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
R2H Day One Internship Expectation Review Guidelines
Quiz
•
Professional Development

12 questions
Dividing Fractions
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

25 questions
Spanish preterite verbs (irregular/changed)
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Identify Slope and y-intercept (from equation)
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

10 questions
Juneteenth: History and Significance
Interactive video
•
7th - 12th Grade

8 questions
"Keeping the City of Venice Afloat" - STAAR Bootcamp, Day 1
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

26 questions
June 19th
Quiz
•
4th - 9th Grade

27 questions
STAAR English 1 Review
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Understanding Linear Equations and Slopes
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade