
Electric Field Line
Quiz
•
Physics
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
+1
Standards-aligned

Charles Martinez
Used 1+ times
FREE Resource
Enhance your content in a minute
14 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt

In the diagram below, P is a point near a negatively charged sphere. Which direction best represents the direction of the electric field at point P?
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS2-4
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which quantity and unit are correctly paired?
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS3-5
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
A point charge Q is far from all other charges. At a distance of 2 m from Q, the electric field is 20 N/C. What is the force a charge of 5 Coulombs feels?
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS2-4
NGSS.HS-PS3-5
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following statements is false about electric field lines
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS4-3
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
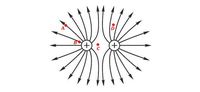
At which point is the electric field the strongest
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS3-5
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt

At which point is the electric field the weakest?
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt

Consider the electric field lines shown in the diagram below. From the diagram, it is apparent that object A is ____ and object B is ____.
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS3-5
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Energy
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
FLUIDA STATIS
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Physical Properties
Quiz
•
7th - 10th Grade

12 questions
World Science Day!
Quiz
•
6th - 10th Grade

15 questions
SESIÓN 19. PRESIÓN
Quiz
•
12th Grade

12 questions
Dinamica 1
Quiz
•
10th Grade

16 questions
SÓNG ÂM - BÀI TẬP
Quiz
•
12th Grade

14 questions
10th Grade Physics Quiz 1
Quiz
•
10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

54 questions
Analyzing Line Graphs & Tables
Quiz
•
4th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

27 questions
Simple Machines and Mechanical Advantage Quiz
Quiz
•
9th Grade

16 questions
Coulomb's Law
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Understanding Heat, Thermal Energy, and Temperature
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Newton's Laws of Motion
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
unit 10 -- electric forces and fields
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

21 questions
Diffraction, Reflection, Refraction
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

