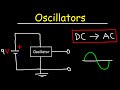
Understanding Oscillators
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Aiden Montgomery
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of an oscillator?
To convert DC input to AC output
To store electrical energy
To convert AC input to DC output
To amplify sound signals
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which type of oscillator produces a sine wave?
Harmonic oscillator
Square wave oscillator
Sawtooth oscillator
Relaxation oscillator
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are the two main components of an oscillator?
Amplifier and feedback network
Diode and transistor
Resistor and capacitor
Inductor and transformer
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What phase shift does the amplifier provide relative to the input signal?
270 degrees
90 degrees
180 degrees
360 degrees
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
According to the Barkhausen criterion, what must the loop gain be for sustained oscillations?
Greater than one
Less than one
Zero
Equal to one
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to oscillations if the loop gain is greater than one?
They die out
They stop immediately
They remain constant
They grow larger and may clip
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which components are typically used in an LC oscillator circuit?
Transformer and resistor
Diode and transistor
Inductor and capacitor
Resistor and capacitor
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Inductive Reactance Quiz
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Inductance and Electromotive Force Concepts
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Ancient Egyptian Mummification and Perfumes
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Acoustic Properties of Ancient Structures
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Resonance in Closed Pipes
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
555 Timer Circuit Waveform Generation
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Electrical Components: Resistance, Reactance, and Impedance
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Resonant Frequency and LC Circuits
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

54 questions
Analyzing Line Graphs & Tables
Quiz
•
4th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

27 questions
Simple Machines and Mechanical Advantage Quiz
Quiz
•
9th Grade

16 questions
Coulomb's Law
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Understanding Heat, Thermal Energy, and Temperature
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Newton's Laws of Motion
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
unit 10 -- electric forces and fields
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

21 questions
Diffraction, Reflection, Refraction
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
10th Grade